Polycarbonate هو بوليمر متعدد الاستخدامات معروف بتوازنه الاستثنائي من الخصائص، مما يجعله أساسياً في الحديث الهندسة و التصنيع.
The unique الكثافة يساهم حوالي 1.2 جم/سم³ في خصائصه خفيفة الوزن مع الحفاظ على القوة الميكانيكية.
تستكشف هذه المقالة كيف polycarbonate’s الكثافة يؤثر على أدائه ولماذا يُفضل في تطبيقات مختلفة تتطلب الشفافية، مقاومة الصدمات، والاستقرار الحراري.
فهم ال الخصائص of البولي كربونات ضروري لاختيار الأفضلية المثلى مادة for specific applications where الوزن الاعتبارات ذات أهمية قصوى.
فهم كثافة مادة البولي كربونات
Understanding the density of polycarbonate is essential for leveraging its unique properties in different fields. Polycarbonate is a versatile thermoplastic polymer known for its exceptional strength, transparency, and resistance to impact.
ما هو البولي كربونات وقيمته الكثافية؟
البوليكربونات هي مجموعة من البوليمرات الحرارية التي تحتوي على مجموعات الكربونات في تراكيبها الكيميائية. تتراوح كثافة مادة البوليكربونات عادةً من 1.19 إلى 1.22 غرام/سم³، مع قيمة مرجعية قياسية تبلغ 1.2 غرام/سم³ تُستخدم في الحسابات الهندسية ومواصفات المواد.
- Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic polymer containing carbonate groups, with bisphenol A (BPA) being a common base component.
- The specific density value of 1.2 g/cm³ places polycarbonate between commodity plastics and high-performance engineering materials.
The Significance of 1.2 g/cm³ in Engineering Applications
الكثافة 1.2 جم/سم³ مهمة بشكل خاص في التطبيقات الهندسية حيث يكون تقليل الوزن حاسماً ولكن لا يمكن التنازل عن الخصائص الميكانيكية. هذه الكثافة، مع قوة الشد العالية (55-75 ميجا باسكال)، تخلق نسبة قوة إلى وزن استثنائية.
- مكونات الفضاء وأجزاء السيارات تستفيد من خصائص البوليكربونات الخفيفة الوزن ولكنها قوية.
- فهم كثافة البوليكربونات أمر حاسم لحساب متطلبات المادة وتوقعات الأداء.
كيف يقارن كثافة البولي كربونات مع البلاستيكات الأخرى
كثافة البوليكربونات هي سمة رئيسية تميزها عن البلاستيكات الأخرى مثل الأكريليك و ABS. فهم هذه الاختلافات ضروري لاختيار المادة المناسبة للتطبيقات المحددة.
Density Comparison: Polycarbonate vs. PMMA (Acrylic)
البولي كربونات لها كثافة تتراوح بين 1.20-1.22 جم/سم³، بينما الـ PMMA (الأكريليك) لها كثافة بين 1.17 و1.20 جم/سم³. على الرغم من أن الفرق في الكثافة ضئيل، إلا أن البولي كربونات توفر مقاومة عالية للصدمات، مما يجعلها أقوى حتى 250 مرة من الأكريليك. هذا الاختلاف في الخصائص الميكانيكية يجعل البولي كربونات الخيار المفضل للتطبيقات التي تتطلب وضوح بصري ومتانة.
As Dr. John Smith, a materials scientist, notes, “The slight density variation between polycarbonate and acrylic translates into substantial differences in their performance characteristics.”
Polycarbonate vs. ABS and Other Engineering Thermoplastics
Compared to ABS, which has a density of approximately 1.05 g/cm³, polycarbonate is about 15% denser. However, polycarbonate provides superior optical clarity, temperature resistance, and impact strength. This makes the slightly higher density of polycarbonate worthwhile for many high-performance applications.
- Polycarbonate offers higher impact resistance compared to ABS.
- البولي كربونات توفر وضوحًا بصريًا أفضل من ABS.
- The temperature resistance of polycarbonate is superior to ABS.
Comparative Density Table of Common Plastics
جدول كثافة مقارن للبوليمرات الشائعة يبرز الموقع النسبي للبوليكربونات بين المواد الأخرى.
| المادة | الكثافة (جم/سم³) |
|---|---|
| Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) | 0.91-0.94 |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | 0.91-0.96 |
| ABS | 1.05 |
| بي إم إم إيه (الأكريليك) | 1.17-1.20 |
| Polycarbonate | 1.20-1.22 |
| PVC | 1.3-1.45 |
As shown in the table, polycarbonate occupies a middle ground between lightweight commodity plastics like polyethylene and heavier engineering materials like PVC. Understanding these density differences is crucial for material selection, as each plastic offers unique advantages based on its density-to-performance ratio.
Physical Properties Influenced by Polycarbonate Density
كثافة البوليكربونات تؤثر بشكل كبير على خصائصها الفيزيائية، مما يجعلها مادة متعددة الاستخدامات لمختلف التطبيقات. ستستعرض هذه القسم كيف تؤثر كثافة البوليكربونات على مقاومة الصدمة، والشفافية، والاستقرار الحراري.
مقاومة الصدمة والمتانة
Polycarbonate is renowned for its exceptional impact resistance, which is directly related to its density. With an Izod impact strength of 600-850 J/m, it is virtually unbreakable in many applications where other materials like glass or acrylic would shatter. The material’s molecular structure and density enable it to absorb and dissipate energy from impacts, providing superior protection in safety-critical applications such as bulletproof windows, protective eyewear, and sports equipment.
Transparency and Optical Properties
Despite its density, polycarbonate achieves remarkable transparency, with light transmission up to 89%. This property makes it outperform many types of glass while weighing approximately half as much. The combination of optical clarity and impact resistance makes polycarbonate ideal for applications requiring both properties, such as in automotive and aerospace industries.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Resistance
Polycarbonate’s thermal stability is directly related to its density and molecular structure. It has a glass transition temperature of about 147°C (297°F) and can withstand temperatures between -40°C and 115-130°C for working applications. This wide temperature range makes polycarbonate suitable for various industrial and consumer applications.
| العقار | القيمة | الوحدة |
|---|---|---|
| الكثافة | 1.2 | جم/سم³ |
| Izod Impact Strength | 600-850 | J/m |
| Light Transmission | Up to 89% | % |
| Glass Transition Temperature | 147 | °C |
Structural Characteristics Behind Polycarbonate’s Density
Understanding the structural characteristics of polycarbonate is crucial for explaining its density. The unique properties of polycarbonate, including its density of 1.2 g/cm³, are directly related to its molecular structure and the arrangement of its polymer chains.
Molecular Structure and Carbonate Groups
The molecular structure of polycarbonate features carbonate groups (-O-(C=O)-O-) that create a rigid backbone. These carbonate linkages have planar OC(OC)2 cores, contributing to the material’s rigidity and thermal stability. The short O=C bond (1.173 Å) and more ether-like C-O bonds (1.326 Å) play a crucial role in polycarbonate’s overall properties.

How Polymer Chains Affect Material Density
The arrangement of polymer chains in polycarbonate results in an amorphous structure, which influences its density and contributes to its optical clarity. Variations in molecular weight during production can fine-tune the material’s density and mechanical properties. Higher molecular weight grades offer increased toughness but are more challenging to process.
| العقار | Effect of Molecular Structure | التأثير على الكثافة |
|---|---|---|
| الصلابة | Carbonate groups create a rigid backbone | Influences overall density |
| الاستقرار الحراري | Planar OC(OC)2 cores contribute to stability | Affects material performance |
| Optical Clarity | Amorphous structure from polymer chain arrangement | Contributes to transparency |
التوازن بين طول السلسلة، والتفرع، والقوى بين الجزيئات في بنية البوليكربونات يخلق الكثافة المثلى التي توفر مزيجها الفريد من القوة، والشفافية، والاستقرار الحراري. فهم هذه الخصائص الهيكلية ضروري للمهندسين للتنبؤ بكيفية أداء البوليكربونات تحت ظروف مختلفة وتعديل خصائصها لتلبية تطبيقات محددة.
Applications Leveraging Polycarbonate’s Density Advantages
The low density of polycarbonate is enabling its use in innovative applications across different industries. Its unique combination of properties, including high impact resistance, transparency, and thermal stability, makes it an ideal material for various sectors.
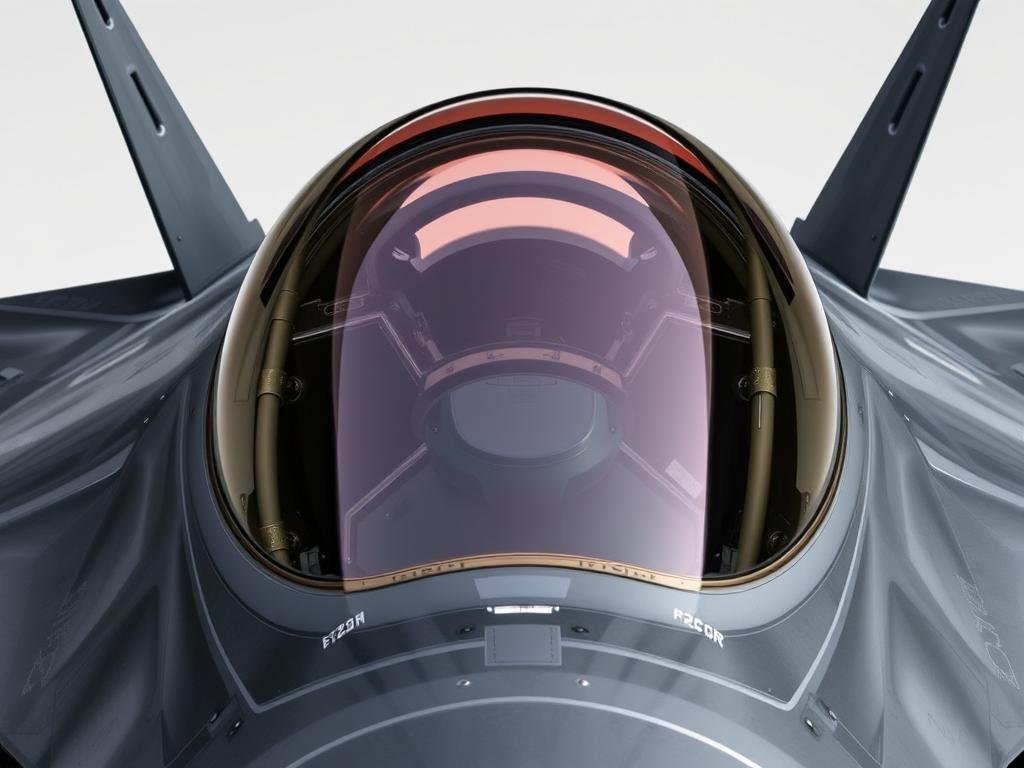
Automotive and Aerospace Applications
Polycarbonate is extensively used in the automotive industry for headlamp عدسات and interior components due to its lightweight and high impact resistance. In aerospace, it is used for cockpit canopies, such as in the F-22 Raptor, benefiting from its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio.

Electronics and Data Storage
The electronics industry leverages polycarbonate’s unique properties for data storage, including CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs. Its precision injection molding creates lightweight yet durable parts.
Construction and Safety Equipment
Polycarbonate sheets are used in construction for greenhouse glazing, skylights, and sound barriers, where transparency, impact resistance, and lightweight properties are required. In safety equipment, polycarbonate is used for protective eyewear, face shields, riot shields, and bulletproof windows, providing protection while remaining lightweight.
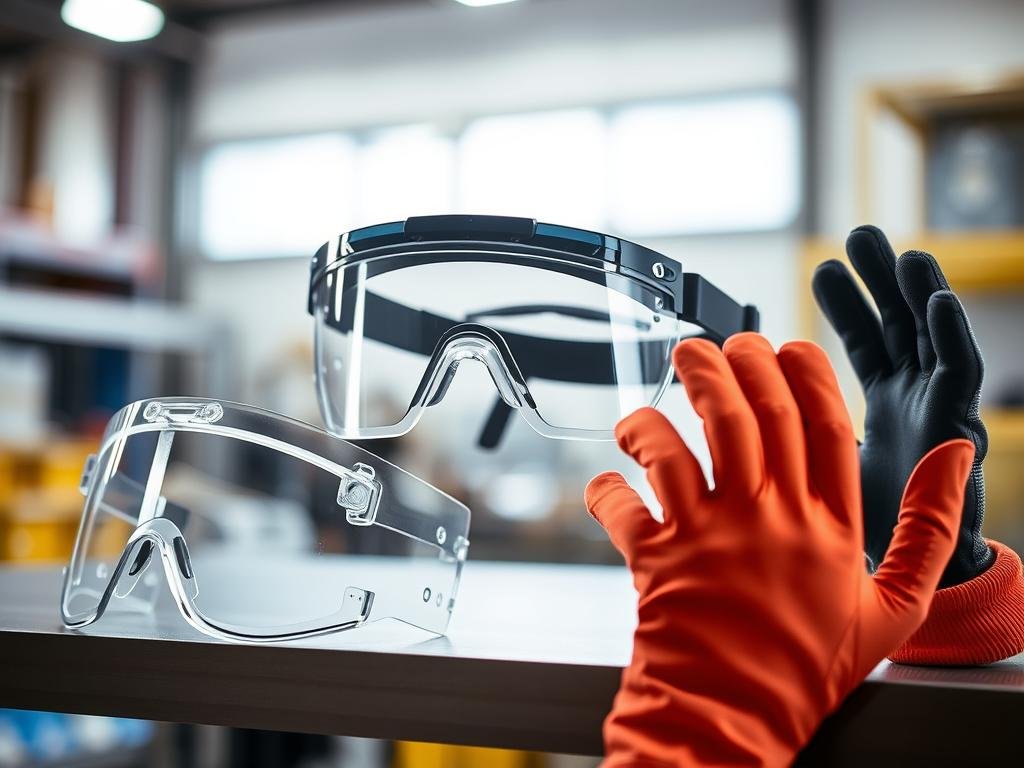

These applications demonstrate the versatility of polycarbonate and its potential to drive innovation in various industries.
Factors That Can Affect Polycarbonate Material Density
Understanding the factors that influence polycarbonate density is crucial for optimizing its performance in different applications. Polycarbonate’s base density of 1.2 g/cm³ can be modified through various means to achieve specific material properties.
تأثير الإضافات والملونات
Additives and fillers play a significant role in altering polycarbonate’s density. For instance, flame retardants can increase density, while impact modifiers may lower it. Foaming agents can be used to create cellular structures that reduce density. The choice of additive depends on the desired application and required material properties.
| Additive/Filler | Effect on Density | تطبيق |
|---|---|---|
| Flame Retardants | Increase | Electrical components |
| Impact Modifiers | انخفض | قطع غيار السيارات |
| Foaming Agents | انخفض | Lightweight structures |
How Processing Methods Influence Density Values
Processing methods such as injection molding, extrusion, and compression molding affect polycarbonate’s density through variations in cooling rates, shear forces, and material flow. Injection molding parameters like pressure, temperature, and cooling rate influence the material’s packing density and internal stress distribution.
Extrusion processes can create materials with more uniform density compared to injection molding. Understanding these variables allows manufacturers to fine-tune polycarbonate’s density for specific applications, balancing weight considerations against mechanical performance requirements.
- Molecular weight directly influences polycarbonate’s density, with higher molecular weight grades exhibiting slightly higher density values.
- Processing conditions that introduce microvoids or internal stresses can reduce the effective density of polycarbonate components.
Potential Concerns Related to Polycarbonate Density
The density of polycarbonate, though advantageous in many applications, also presents potential environmental and health risks. While its lightweight and tough properties make it an ideal material for various industries, its density and chemical structure contribute to its resistance to natural degradation in landfills.
Environmental Impact and Degradation
Polycarbonate’s resistance to degradation raises concerns about its environmental impact. The material can hydrolyze to bisphenol A (BPA) under certain conditions, such as high temperatures and humidity, potentially releasing harmful compounds into the environment. Moreover, the leaching of BPA from polycarbonate can occur even at environmental temperatures and normal pH levels, posing risks to ecosystems and human health.
BPA Concerns in Food-Contact Applications
In food-contact applications, the potential migration of BPA from polycarbonate products has raised safety concerns. This has led manufacturers to develop BPA-free polycarbonate alternatives that maintain similar density and mechanical properties. However, the challenge remains to balance the benefits of polycarbonate’s density with the need to minimize its environmental footprint and ensure safety in various applications.
الخلاصة: مستقبل البوليكربونات كمادة هندسية خفيفة الوزن
مستقبل البولي كربونات نظرًا لأن مادة الهندسة خفيفة الوزن الرائدة تبدو واعدة، مدفوعة بالأبحاث المستمرة والابتكارات في عمليات التصنيع. مع its الكثافة من 1.2 جم/سم³ البولي كربونات يقدم توازناً مثالياً من الخصائص التي تدفع الابتكار عبر صناعات متعددة حيث خفيف الوزن و عالي-مواد القوة ضرورية.
التطورات في عمليات التصنيع تمكين تحكم أكثر دقة على كثافة البوليكربونات، مما يسمح بالتخصيص المواد التي تلبي متطلبات محددة المتطلبات لـ الوزن, قوة، والبصرية الجودة. مع استمرار المهندسين في الاستفادة polycarbonate’s فريد الكثافة الخصائص، المستقبل التطبيقات من المحتمل أن يتوسع ليشمل مجالات جديدة، بما في ذلك الأجهزة الطبية المتقدمة وأنظمة النقل من الجيل التالي.
