理解的 熔點 聚丙烯對於各種工業應用來說至關重要。這種熱塑性聚合物以其耐用性和耐熱性而聞名,成為製造商的熱門選擇。
The 溫度 聚丙烯的熔點通常介於130°C到171°C(266°F到340°F)之間。這相對較高 熔點 允許聚丙烯在高溫下保持其強度和剛性,使其適用於各種工業用途。
在我們探索聚丙烯的特性與應用時,顯示其熱性質在選擇耐溫應用材料方面扮演著重要角色。
Understanding Polypropylene and Its Properties
要了解聚丙烯,我們首先需要探索它的基本特性。聚丙烯是一種熱塑性材料 聚合物 belonging to the polyolefin family, known for its versatility and wide range of applications.
聚丙烯是什麼?
Polypropylene (PP) is produced through the polymerization of propylene monomers. It is characterized by its light weight, high 力量, and good 抗拒 to chemicals and heat. PP appears as white granules, is odorless, and non-toxic. Its molecular structure is similar to polyethylene but with a methyl group attached to alternate carbon atoms, contributing to its unique 屬性.
Key Characteristics of Polypropylene
聚丙烯具有幾個關鍵特性,使其具有價值 material 在各行各業中。它具有良好的拉伸性 力量 and rigidity, although its impact 力量 相對較差,尤其在低溫下。PP 以其低水分而聞名 吸收 匯率(24小時後為0.01%),有助於其尺寸穩定性和電氣絕緣性 屬性. 此外,它的密度較低(0.90-0.91 g/cm³),使其成為最輕的商業產品之一 塑膠, offering significant weight advantages. However, it has limitations such as poor UV 抗拒 以及有限的熱量 抗拒 與工程熱塑性塑料相比。

聚丙烯的熔點範圍
Polypropylene’s melting behavior is a critical aspect of its application in various industries. The melting point of polypropylene is not a single value but rather a range, typically between 130°C to 171°C (266°F to 340°F).
Standard Melting Temperature Range
聚丙烯的標準熔點範圍通常被認為是在160°C到170°C(320°F到338°F)之間。此範圍可能會根據聚丙烯的特定等級及其結晶結構而有所變化。 差示掃描量熱法 (DSC) 是一種用來判定聚丙烯熔融特性的常見技術。
| Property | Value | 單位 |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point Range | 130-171 | °C |
| 典型熔點範圍 | 160-170 | °C |
| 滅菌溫度 | 100以上 | °C |
融點與玻璃轉變溫度有何不同
熔點和玻璃轉變溫度是兩個不同的熱性質。熔點是聚丙烯由固體轉變為液體的溫度,而玻璃轉變溫度則是聚合物非晶區域變得較不僵硬的點。對於聚丙烯來說,玻璃轉變溫度通常約在0°C到10°C(32°F到50°F)之間,遠低於其熔點。
Factors Affecting Polypropylene’s Melting Point
The thermal properties of polypropylene, particularly its melting point, are affected by multiple factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing its performance in various applications.
Molecular Weight and Structure
聚丙烯的分子量與結構在決定其熔點方面扮演著重要角色。具有較高分子量的聚丙烯通常具有較高的熔點,因為其分子間作用力較強。聚合物鏈中甲基基團的空間排列方式,不論是等規、反規或非規,也會影響其熔融行為與結晶潛能。
- 較高分子量的聚丙烯通常具有較高的熔點。
- The molecular structure affects the polymer’s crystallization potential and thermal properties.
Crystallinity and Its Impact
The degree of crystallinity in polypropylene directly impacts its melting point. More highly crystalline grades require higher temperatures to melt due to their ordered molecular structure. Nucleating agents can be used to control crystallization, thereby influencing both the melting point and the overall thermal performance of polypropylene products.
Effect of Additives and Fillers
聚丙烯常與各種添加劑和填充物一起使用,以改變其性質。某些穩定劑可以提高熔點,使其更適合高溫應用。填充物和增強劑,例如滑石粉、碳酸鈣和玻璃纖維,可以改變聚丙烯化合物的熱行為,可能提高或降低其有效熔點。
- Additives like antioxidants and UV stabilizers can impact polypropylene’s melting characteristics.
- Copolymerization with other monomers, such as ethylene, can adjust polypropylene’s melting point for specific applications.
Processing Polypropylene at Optimal Temperatures
Achieving optimal results when processing polypropylene requires a deep understanding of its temperature requirements. When molding or extruding polypropylene, it’s essential to set equipment to a temperature above its melting point, typically between 160°C to 170°C (320°F to 338°F), for optimal flow and quality.
Injection Molding Temperature Considerations
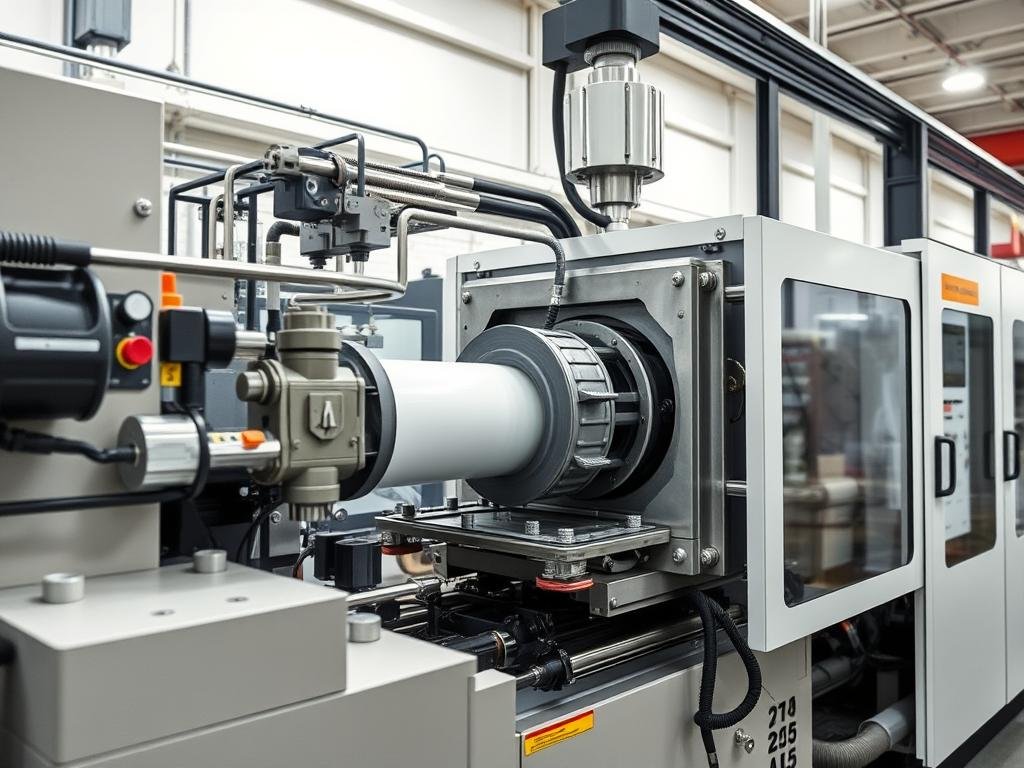

For injection molding, precise temperature control is crucial. The barrel temperature profile and mold temperature settings significantly affect the flow characteristics and final part properties. Adjusting these parameters according to the specific grade of polypropylene being used is vital for achieving the desired product quality.
Extrusion and Other Processing Methods
In extrusion processing, maintaining the right temperature profile across different zones of the extruder and die temperature is critical. Other processing methods like blow molding, thermoforming, and rotational molding also require specific temperature guidelines. Proper cooling rates are essential to ensure the material achieves the desired properties.
By understanding the optimal processing temperatures for polypropylene and adjusting processing conditions accordingly, manufacturers can ensure high-quality products with desired mechanical properties.
Comparing Polypropylene’s Melting Point to Other Polymers
When selecting materials for a project, comparing the melting points of polypropylene and other polymers is essential. This comparison helps in understanding the suitability of these materials for various applications, especially those involving elevated temperatures.
聚丙烯與聚乙烯
聚丙烯(PP)的熔點約為160至170攝氏度,而高密度聚乙烯(HDPE)的熔點約為130至140攝氏度,低密度聚乙烯(LDPE)的熔點則在105至115攝氏度。聚丙烯分子結構中甲基基團的存在,使其熔點高於聚乙烯。
這個熔點的差異在實際應用適用性上產生了差異。例如,聚丙烯更適合需要暴露在較高溫度下的應用,儘管它並不被認為具有高度耐溫性。
聚丙烯與較高溫度聚合物
與尼龍(PA)、聚酯(PET)、聚碳酸酯(PC)和聚醚醚酮(PEEK)等高溫工程熱塑性塑料相比,聚丙烯的熔點相對較低。這些差異對於加工需求、設備需求和製造過程中的能量消耗具有重要影響。
下表提供常見熱塑性塑料的熔點比較:
| Polymer | 熔點 (°C) |
|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | 160-170 |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | 130-140 |
| Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) | 105-115 |
| 尼龍 (PA) | 220-260 |
| 聚醚醚酮 (PEEK) | 343 |
了解這些差異對於材料選擇與加工至關重要。相對熔點不僅影響製造過程,也影響最終產品在特定應用中的適用性。
應用利用聚丙烯的熱性能
由於其獨特的熔點和耐熱性,聚丙烯在多個產業的許多高價值應用中被使用。它的多功能性來自於能夠承受各種溫度,使其適用於廣泛的用途。
汽車與工業應用
聚丙烯在汽車產業中被廣泛用於製造零件,例如保險桿、儀表板、車門飾板和頭燈外殼。它的輕量、高強度和耐化學性使其成為這些應用的理想材料。

食品包裝與消費者產品
在食品包裝中,聚丙烯的耐熱性能允許熱灌裝、微波使用和熱水滅菌,同時保持產品的完整性與安全性。它用於製作食品包裝袋、保鮮膜、飲料瓶和食品容器。
醫療與高性能應用
聚丙烯由於其無毒、耐熱和化學穩定性,被用於醫療設備,如注射器、靜脈輸液袋和藥瓶。在這些應用中,能夠承受消毒溫度而不降解的能力至關重要。
聚丙烯的多樣應用凸顯了其作為多功能且具有成本效益的材料的價值。其熱性能在各行各業的性能與耐用性方面具有重要貢獻。
結論:聚丙烯熔點的實際應用意義
聚丙烯的熱穩定性,以其熔點為特徵,是其在各種工業應用中選擇的關鍵因素。聚丙烯的熔融範圍為130°C至171°C,提供多樣用途的彈性,同時在加工過程中需要精確的溫度控制。 製造.
了解聚丙烯的熔融行為使製造商能夠優化加工參數、提升產品品質,並降低生產成本。其在熱性能與成本效益之間的平衡,使聚丙烯成為適用於需要適度性能的應用的理想材料 耐熱性.
隨著產業的不斷演進,聚丙烯開發的進步,包括共聚物和複合材料,預計將提升其熱性能。通過考慮聚丙烯的熔點,工程師和設計師可以開發符合特定熱需求的新產品,推動其在各個行業的持續應用。
