Stainless steel is often considered resistant to corrosion and degradation, but many homeowners wonder if it can develop mold under certain conditions.
Mold spores are ubiquitous and can survive even in extreme environments. While stainless steel is generally resistant to microbial growth, it’s not entirely immune to mold issues.
Understanding the factors that contribute to mold growth on metal surfaces is crucial for maintaining the longevity and appearance of your stainless steel appliances and fixtures.
This comprehensive guide will explore the relationship between stainless steel and mold, providing practical insights and actionable strategies for identifying, removing, and preventing mold on stainless steel surfaces.
Understanding Stainless Steel and Its Properties
Stainless steel’s broad range of applications stems from its impressive combination of strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal. This alloy is primarily composed of iron, chromium, and sometimes other elements, which together provide its notable properties.
What Makes Stainless Steel “Stainless”
The presence of chromium is what makes stainless steel “stainless.” Chromium forms a thin, transparent layer of oxide on the surface, protecting the underlying metal from corrosion. This characteristic is crucial in areas exposed to moisture, making it ideal for use in various environments.
Common Applications of Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is utilized in diverse industries due to its beneficial properties. Some common applications include:
- Kitchen appliances and cookware, where its durability and hygienic properties are valued.
- Bathroom fixtures like faucets and shower heads, which benefit from its resistance to water damage.
- The medical and food industries, where its non-reactive nature is essential for equipment and utensils.
- Architectural features such as building facades and structural components, particularly in environments where corrosion resistance is crucial.
- Transportation industries, for vehicle components that require high strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to harsh environmental conditions.
In these areas, stainless steel’s unique properties provide significant advantages, making it a preferred material in the presence of moisture and other challenging environment factors.
Does Stainless Steel Mold? The Truth Revealed
Understanding if and how mold grows on stainless steel is crucial for various applications, from kitchen appliances to industrial equipment. While stainless steel is known for its resistance to corrosion and durability, the question remains whether it can support mold growth.
The Science Behind Mold Growth
Mold growth is facilitated by the presence of moisture, nutrients, and suitable temperatures. Although stainless steel itself does not provide nutrients for mold, its surface can accumulate organic matter that serves as a food source. The interaction between mold and stainless steel is primarily superficial, with mold colonies forming on residue rather than the metal itself.
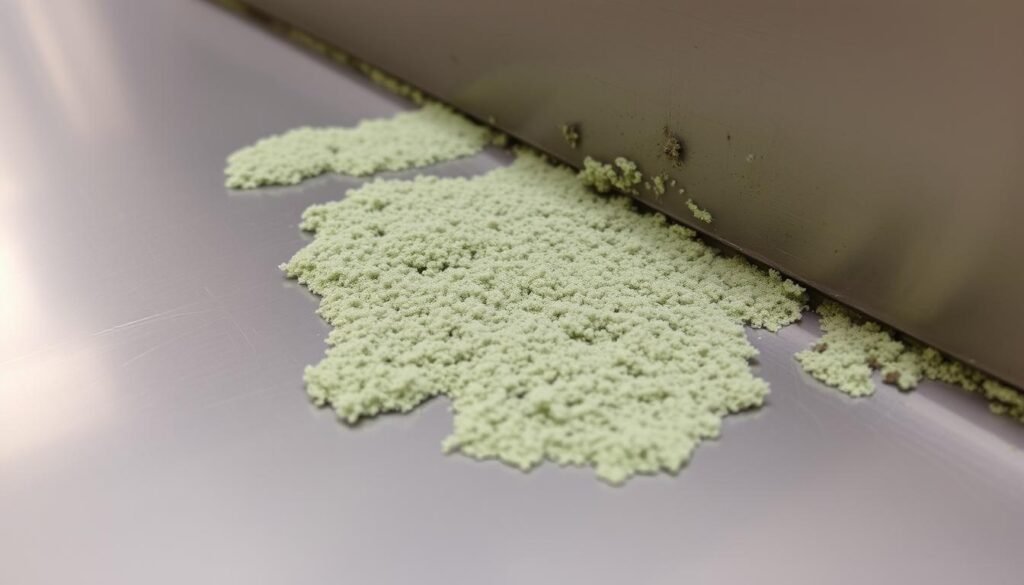

How Mold Interacts with Metal Surfaces
The surface characteristics of stainless steel play a significant role in mold growth. Microscopic imperfections can trap moisture and organic particles, creating micro-environments conducive to mold establishment. While the chromium oxide layer protects stainless steel from corrosion and mold penetration, it cannot prevent surface colonization when conditions are favorable.
- Mold growth on stainless steel is often a result of surface contamination.
- The chromium oxide layer on stainless steel provides protection against mold penetration.
Conditions That Promote Mold Growth on Stainless Steel
Understanding the conditions that promote mold growth on stainless steel is crucial for prevention. Several factors contribute to creating an environment where mold can thrive on stainless steel surfaces.
Moisture and Humidity Factors
High moisture and humidity levels are significant contributors to mold growth on stainless steel. Areas like bathrooms and kitchens, where humidity is typically higher, are more prone to mold issues if not properly ventilated. Excess moisture creates an ideal environment for mold spores to germinate.
Organic Residue Accumulation
The accumulation of organic residue on stainless steel surfaces also plays a critical role in mold growth. When organic matter is present, it provides a nutrient source for mold, facilitating its growth. Regular cleaning is essential to prevent the buildup of such residues.
Poor Ventilation Issues
If air isn’t circulating properly, it creates a stagnant environment where moisture lingers, making it an ideal place for mold to grow. Key issues include:
- Inadequate air circulation that prevents moisture evaporation from stainless steel surfaces.
- Enclosed spaces with stainless steel fixtures being particularly vulnerable to mold when ventilation is poor.
- The combination of high humidity and restricted airflow creating microclimates that support mold growth.
Common Areas Where Mold Grows on Stainless Steel
Mold can surprisingly grow on stainless steel surfaces, particularly in areas with high moisture. This growth is often seen in household areas where water is frequently used.
Kitchen Appliances and Sinks
In the kitchen, mold can grow on stainless steel appliances and sinks, especially around areas where water tends to stagnate. Regular cleaning is essential to prevent mold growth in these areas.
- Sinks with poor drainage can accumulate water, creating an ideal environment for mold.
- Kitchen appliances, such as dishwashers and refrigerators, can develop mold around seals and joints.
Bathroom Fixtures
Bathrooms are particularly prone to mold due to high humidity levels and constant water exposure. 
- Shower heads and faucets frequently develop mold around joints and aerators.
- Stainless steel towel bars and hooks can also develop mold, especially where they connect to walls.
Regular maintenance and ensuring good ventilation can help mitigate mold growth in these areas where mold stainless steel is commonly found.
How to Identify Mold on Stainless Steel
Identifying mold on stainless steel surfaces is crucial for maintaining cleanliness and preventing health risks. Mold can grow on stainless steel under certain conditions, and its identification requires attention to detail.
Visual Signs of Mold Growth
Mold on stainless steel can manifest in various ways. It often appears as a soft, sometimes slimy, growth on the surface. The color can range from black, green, to white, depending on the type of mold and the surface conditions. In some cases, mold may be mistaken for other stains or residue, making a closer inspection necessary.
Distinguishing Mold from Other Stains
Distinguishing mold from other stains on steel involves observing the stain’s texture, color, and response to cleaning. Unlike water spots or mineral deposits, mold tends to persist even after wiping with a damp cloth. A simple test involves applying a drop of household bleach; if the stain is mold, it will typically lighten or disappear within 1-2 minutes. Additionally, mold often has a characteristic growth pattern, unlike food stains or rust, which have distinct appearances and textures.
Effective Methods to Remove Mold from Stainless Steel
To eliminate mold from stainless steel surfaces, it’s crucial to use effective cleaning methods that target the root cause of the issue. A comprehensive approach involves neutralizing fungi, cleaning the metal surface, restoring the metal coating, and protecting the surface from future contamination.
Vinegar-Based Cleaning Solutions
Vinegar is a natural and effective cleaning agent for removing mold from stainless steel. Mix equal parts of water and white vinegar in a spray bottle. Spray the solution onto the moldy area and let it sit for about 10 minutes. The acid in the vinegar helps break down the mold, making it easier to remove.
Step-by-Step Cleaning Process
Start by applying the vinegar-based cleaning solution to the affected area. Let it sit before scrubbing gently with a soft-bristled brush. Rinse the area thoroughly with warm water and dry it with a clean towel to prevent water spots. This step-by-step cleaning process ensures the removal of mold and helps maintain the integrity of the stainless steel surface.
When to Use Commercial Cleaners
For more severe mold infestations, commercial mold removers may be necessary. Look for products containing quaternary ammonium compounds or oxygen bleach, which are effective against mold on stainless steel. Always test a small, inconspicuous area first to ensure the cleaner doesn’t damage the metal’s protective layer.
Preventing Mold Growth on Stainless Steel
Mold prevention on stainless steel requires a combination of good maintenance habits and environmental control. By adopting these strategies, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of mold growth on stainless steel surfaces in your home or business.
Regular Maintenance Practices
Regular cleaning and drying of stainless steel surfaces are crucial in preventing mold growth. Ensure that your kitchen or bathroom is well-ventilated by opening windows or using exhaust fans as needed. Fix any leaks or drips promptly to prevent moisture from lingering on surfaces. After use, dry out your sink and countertops to prevent water from pooling.
- Wipe down stainless steel surfaces regularly to remove any debris or residue.
- Use a clean, dry cloth to dry surfaces after cleaning.
Environmental Controls
Controlling the environment around stainless steel fixtures is also vital. Maintain indoor humidity levels between 30-50% using dehumidifiers in moisture-prone areas to create an environment inhospitable to mold spores. Install and regularly use exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms to remove excess moisture from the air.
- Address water leaks promptly to prevent persistent moisture conditions.
- Improve air circulation around stainless steel fixtures by ensuring adequate spacing between appliances.
Conclusion
To keep stainless steel fixtures and appliances mold-free, regular maintenance is crucial. While stainless steel is more resistant to mold than many materials, it’s not completely immune under the right conditions of moisture and organic residue. Understanding that mold interactions occur primarily on surface contaminants is key to effective prevention.
By implementing effective cleaning techniques and controlling environmental factors like humidity, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of mold growth. Using solutions like vinegar or baking soda can help eliminate mold when it appears. Regular cleaning is a minimal investment compared to removing established mold colonies.
